Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Algorithm: MEStaticProjection#
:: _label_algorithm_ME_static_projection:
# Windows users have to encapsulate the code into a main function to avoid multiprocessing errors.
# def main():
import pygpc
from collections import OrderedDict
fn_results = 'tmp/mestaticprojection' # filename of output
save_session_format = ".pkl" # file format of saved gpc session ".hdf5" (slow) or ".pkl" (fast)
Loading the model and defining the problem#
# define model
model = pygpc.testfunctions.DiscontinuousRidgeManufactureDecay()
# define problem
parameters = OrderedDict()
parameters["x1"] = pygpc.Beta(pdf_shape=[1, 1], pdf_limits=[0, 1])
parameters["x2"] = pygpc.Beta(pdf_shape=[1, 1], pdf_limits=[0, 1])
problem = pygpc.Problem(model, parameters)
Setting up the algorithm#
# gPC options
options = dict()
options["method"] = "reg"
options["solver"] = "LarsLasso"
options["settings"] = None
options["order"] = [5, 5]
options["order_max"] = 5
options["interaction_order"] = 2
options["n_cpu"] = 0
# options["gradient_enhanced"] = False
# options["gradient_calculation"] = "FD_fwd"
# options["gradient_calculation_options"] = {"dx": 0.001, "distance_weight": -2}
options["error_type"] = "nrmsd"
options["n_samples_validation"] = 1e3
options["qoi"] = "all"
options["classifier"] = "learning"
options["classifier_options"] = {"clusterer": "KMeans",
"n_clusters": 2,
"classifier": "MLPClassifier",
"classifier_solver": "lbfgs"}
options["fn_results"] = fn_results
options["save_session_format"] = save_session_format
options["grid"] = pygpc.Random
options["grid_options"] = {"seed": 1}
options["n_grid"] = 2000
options["adaptive_sampling"] = False
# define algorithm
algorithm = pygpc.MEStaticProjection(problem=problem, options=options)
Running the gpc#
# Initialize gPC Session
session = pygpc.Session(algorithm=algorithm)
# run gPC algorithm
session, coeffs, results = session.run()
Creating initial grid (Random) with n_grid=2000
Determining gPC approximation for QOI #0:
=========================================
Performing 2000 simulations!
It/Sub-it: 5/2 Performing simulation 0001 from 2000 [ ] 0.1%
Total function evaluation: 0.0006284713745117188 sec
It/Sub-it: 5/2 Performing simulation 0001 from 4000 [ ] 0.0%
Gradient evaluation: 0.03206920623779297 sec
Determine gPC coefficients using 'LarsLasso' solver ...
Determine gPC coefficients using 'LarsLasso' solver ...
-> relative nrmsd error = 0.017544137787869722
Determining gPC approximation for QOI #1:
=========================================
Determine gPC coefficients using 'LarsLasso' solver ...
Determine gPC coefficients using 'LarsLasso' solver ...
-> relative nrmsd error = 0.017544137787869722
Postprocessing#
# read session
session = pygpc.read_session(fname=session.fn_session, folder=session.fn_session_folder)
# Post-process gPC
pygpc.get_sensitivities_hdf5(fn_gpc=options["fn_results"],
output_idx=None,
calc_sobol=True,
calc_global_sens=True,
calc_pdf=True,
algorithm="sampling",
n_samples=1e3)
> Loading gpc session object: tmp/mestaticprojection.pkl
> Loading gpc coeffs: tmp/mestaticprojection.hdf5
> Adding results to: tmp/mestaticprojection.hdf5
Validation#
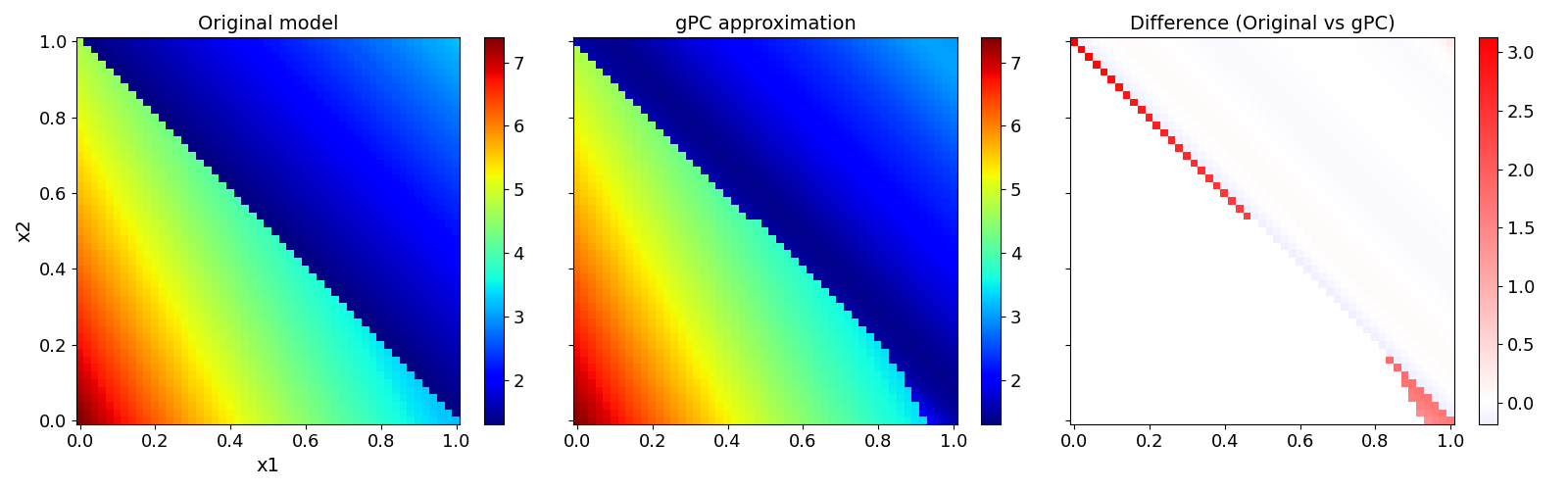
Validate gPC vs original model function (2D-surface)#
pygpc.validate_gpc_plot(session=session,
coeffs=coeffs,
random_vars=list(problem.parameters_random.keys()),
n_grid=[51, 51],
output_idx=[0],
fn_out=None,
folder=None,
n_cpu=session.n_cpu)
Validate gPC vs original model function (Monte Carlo)#
nrmsd = pygpc.validate_gpc_mc(session=session,
coeffs=coeffs,
n_samples=int(1e4),
output_idx=[0],
fn_out=None,
folder=None,
plot=True,
n_cpu=session.n_cpu)
print("> Maximum NRMSD (gpc vs original): {:.2}%".format(max(nrmsd)))
# On Windows subprocesses will import (i.e. execute) the main module at start.
# You need to insert an if __name__ == '__main__': guard in the main module to avoid
# creating subprocesses recursively.
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# main()
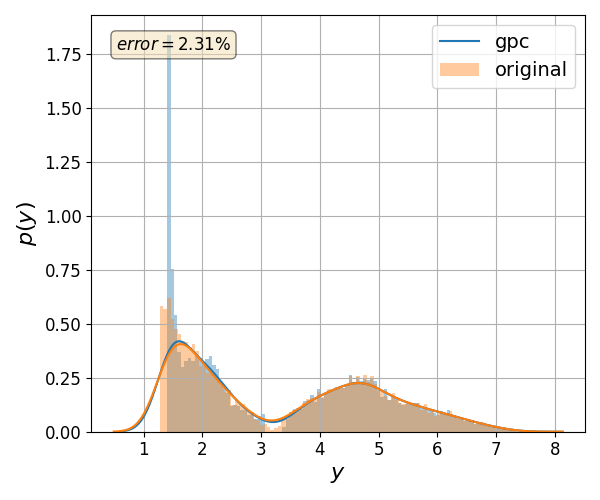
> Maximum NRMSD (gpc vs original): 0.023%
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 17.702 seconds)