Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Algorithm: Static_IO#
# Windows users have to encapsulate the code into a main function to avoid multiprocessing errors.
# def main():
import pygpc
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
# matplotlib.use("Qt5Agg")
from collections import OrderedDict
fn_results = 'tmp/static_IO' # filename of output
save_session_format = ".pkl" # file format of saved gpc session ".hdf5" (slow) or ".pkl" (fast)
np.random.seed(1)
Setup input and output data#
# We artificially generate some coordinates for the input data the user has to provide where the model was sampled
n_grid = 100
x1 = np.random.rand(n_grid) * 0.8 + 1.2
x2 = 1.25
x3 = np.random.rand(n_grid) * 0.6
# define the properties of the random variables
parameters = OrderedDict()
parameters["x1"] = pygpc.Beta(pdf_shape=[1, 1], pdf_limits=[1.2, 2])
parameters["x3"] = pygpc.Beta(pdf_shape=[1, 1], pdf_limits=[0, 0.6])
# generate a grid object from the input data
grid = pygpc.RandomGrid(parameters_random=parameters, coords=np.vstack((x1,x3)).T)
# get output data (here: Peaks function)
results = (3.0 * (1 - x1) ** 2. * np.exp(-(x1 ** 2) - (x3 + 1) ** 2)
- 10.0 * (x1 / 5.0 - x1 ** 3 - x3 ** 5)
* np.exp(-x1 ** 2 - x3 ** 2) - 1.0 / 3
* np.exp(-(x1 + 1) ** 2 - x3 ** 2)) + x2
results = results[:, np.newaxis]
Setting up the algorithm#
# gPC options
options = dict()
options["method"] = "reg"
options["solver"] = "LarsLasso"
options["settings"] = None
options["order"] = [9, 9]
options["order_max"] = 9
options["interaction_order"] = 2
options["error_type"] = "loocv"
options["n_samples_validation"] = None
options["fn_results"] = fn_results
options["save_session_format"] = save_session_format
options["backend"] = "omp"
options["verbose"] = True
# determine number of gPC coefficients (hint: compare it with the amount of output data you have)
n_coeffs = pygpc.get_num_coeffs_sparse(order_dim_max=options["order"],
order_glob_max=options["order_max"],
order_inter_max=options["interaction_order"],
dim=len(parameters))
# define algorithm
algorithm = pygpc.Static_IO(parameters=parameters, options=options, grid=grid, results=results)
Running the gpc#
# initialize gPC Session
session = pygpc.Session(algorithm=algorithm)
# run gPC algorithm
session, coeffs, results = session.run()
> Determining 55 gPC coeffs with 100 simulations!
Determine gPC coefficients using 'LarsLasso' solver ...
LOOCV 01 from 25 [= ] 4.0%
LOOCV 02 from 25 [=== ] 8.0%
LOOCV 03 from 25 [==== ] 12.0%
LOOCV 04 from 25 [====== ] 16.0%
LOOCV 05 from 25 [======== ] 20.0%
LOOCV 06 from 25 [========= ] 24.0%
LOOCV 07 from 25 [=========== ] 28.0%
LOOCV 08 from 25 [============ ] 32.0%
LOOCV 09 from 25 [============== ] 36.0%
LOOCV 10 from 25 [================ ] 40.0%
LOOCV 11 from 25 [================= ] 44.0%
LOOCV 12 from 25 [=================== ] 48.0%
LOOCV 13 from 25 [==================== ] 52.0%
LOOCV 14 from 25 [====================== ] 56.0%
LOOCV 15 from 25 [======================== ] 60.0%
LOOCV 16 from 25 [========================= ] 64.0%
LOOCV 17 from 25 [=========================== ] 68.0%
LOOCV 18 from 25 [============================ ] 72.0%
LOOCV 19 from 25 [============================== ] 76.0%
LOOCV 20 from 25 [================================ ] 80.0%
LOOCV 21 from 25 [================================= ] 84.0%
LOOCV 22 from 25 [=================================== ] 88.0%
LOOCV 23 from 25 [==================================== ] 92.0%
LOOCV 24 from 25 [====================================== ] 96.0%
LOOCV 25 from 25 [========================================] 100.0%
LOOCV computation time: 0.12250995635986328 sec
-> relative loocv error = 2.1539488393624837e-05
Postprocessing#
# read session
session = pygpc.read_session(fname=session.fn_session, folder=session.fn_session_folder)
# Post-process gPC
pygpc.get_sensitivities_hdf5(fn_gpc=options["fn_results"],
output_idx=None,
calc_sobol=True,
calc_global_sens=True,
calc_pdf=True,
algorithm="standard")
# get a summary of the sensitivity coefficients
sobol, gsens = pygpc.get_sens_summary(fn_results, parameters)
print(sobol)
print(gsens)
# plot gPC approximation and IO data
pygpc.plot_gpc(session=session,
coeffs=coeffs,
random_vars=["x1", "x3"],
output_idx=0,
n_grid=[100, 100],
coords=grid.coords,
results=results)
# On Windows subprocesses will import (i.e. execute) the main module at start.
# You need to insert an if __name__ == '__main__': guard in the main module to avoid
# creating subprocesses recursively.
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# main()
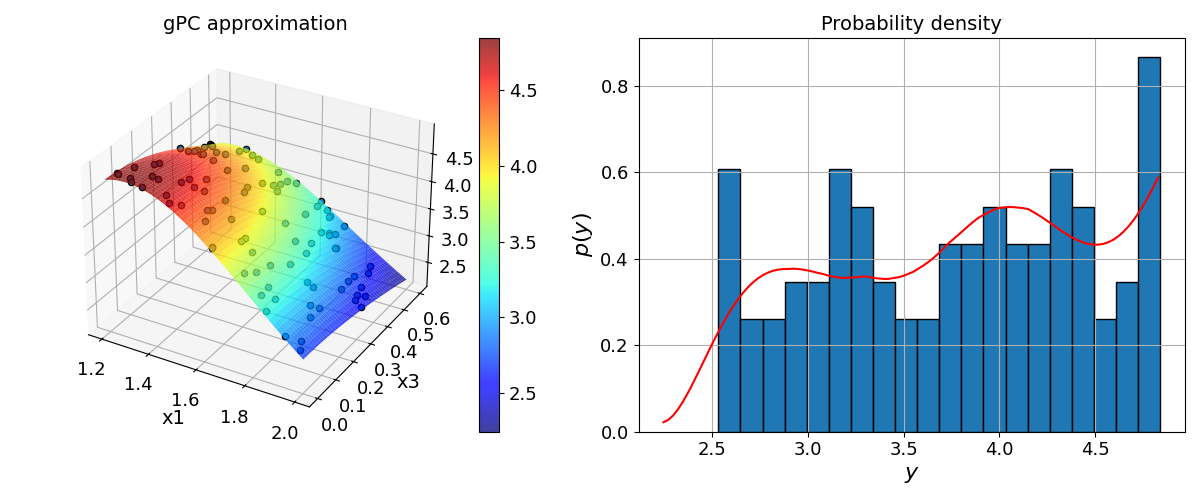
> Loading gpc session object: tmp/static_IO.pkl
> Loading gpc coeffs: tmp/static_IO.hdf5
> Adding results to: tmp/static_IO.hdf5
sobol_norm (qoi 0)
['x1'] 0.861758
['x3'] 0.131113
['x1', 'x3'] 0.007129
global_sens (qoi 0)
x1 -0.958690
x3 -0.402739
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.815 seconds)