Note
Click here to download the full example code
Parallel processing capabilities of pygpc#
pygpc is capable of to evaluate multiple sampling points, i.e. multiple model instances, in parallel. Depending on your model and its hardware requirements there exist three ways to evaluate your model controlled by the algorithm options “n_cpu”:
n_cpu = 0: Use this option if your model is capable of to evaluate sampling points in parallel. In this way, arrays are passed to your model for each parametern_cpu = 1: The model is called in serial for every sampling point. A single floating point number is passed for each parameter.n_cpu > 1: A multiprocessing.Pool will be opened and n_cpu sampling points are calculated in parallel. In each thread, a single floating point number is passed for each parameter.
Example#
# Windows users have to encapsulate the code into a main function to avoid multiprocessing errors.
# def main():
import time
import pygpc
import numpy as np
import multiprocessing
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from collections import OrderedDict
SurfaceCoverageSpecies = pygpc.SurfaceCoverageSpecies()
# generate grid with 1000 sampling points
grid = pygpc.Random(parameters_random=SurfaceCoverageSpecies.problem.parameters_random, n_grid=100)
# define different values for n_cpu
n_cpu_list = [0, 1, multiprocessing.cpu_count()]
t_eval = dict()
# evaluate model with different values for n_cpu
for n_cpu in n_cpu_list:
# initialize computation class; this is done in the algorithm with options["n_cpu"]
com = pygpc.Computation(n_cpu=n_cpu)
# run model and determine computation time
t_n_cpu = []
start = time.time()
res = com.run(model=SurfaceCoverageSpecies.model, problem=SurfaceCoverageSpecies.problem, coords=grid.coords)
stop = time.time()
t_eval[str(n_cpu)] = stop - start
# plot results
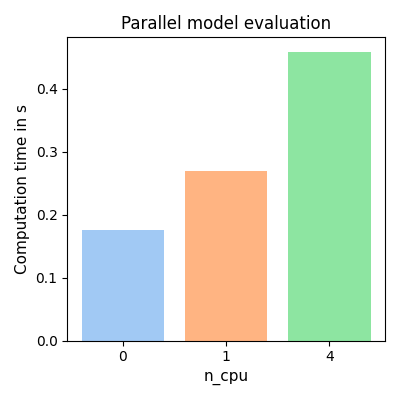
plt.figure(figsize=[4, 4])
for ind, t in enumerate(t_eval):
plt.bar(ind, t_eval[t], color=sns.color_palette("pastel", len(t_eval))[ind])
plt.xlabel("n_cpu", fontsize=11)
plt.ylabel("Computation time in s", fontsize=11)
plt.xticks(range(len(t_eval)), t_eval.keys())
plt.title("Parallel model evaluation", fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
# On Windows subprocesses will import (i.e. execute) the main module at start.
# You need to insert an if __name__ == '__main__': guard in the main module to avoid
# creating subprocesses recursively.
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# main()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.577 seconds)